The Method
The Spiral Stabilization method was invented by Doctor Richard Smíšek in 1979, and it continues to be developed and refined by him and his two daughters Kateřina and Zuzana. The Spiral Stabilization is a set of exercises to help improve the musculoskeletal system and restore its function. The exercises are performed with an elastic cord that helps strengthening the muscle corset, enhances endurance, and improves posture.
Principles
- Vertical axis
- Muscle balance in trunk and girdles
- Sufficient range of motion
- Spiral stabilization

Strengthen the muscle corset
Eliminate muscle imbalances
Relax the muscles
Stretch the spine upwards
Improve posture
Increase the range of motion of the body
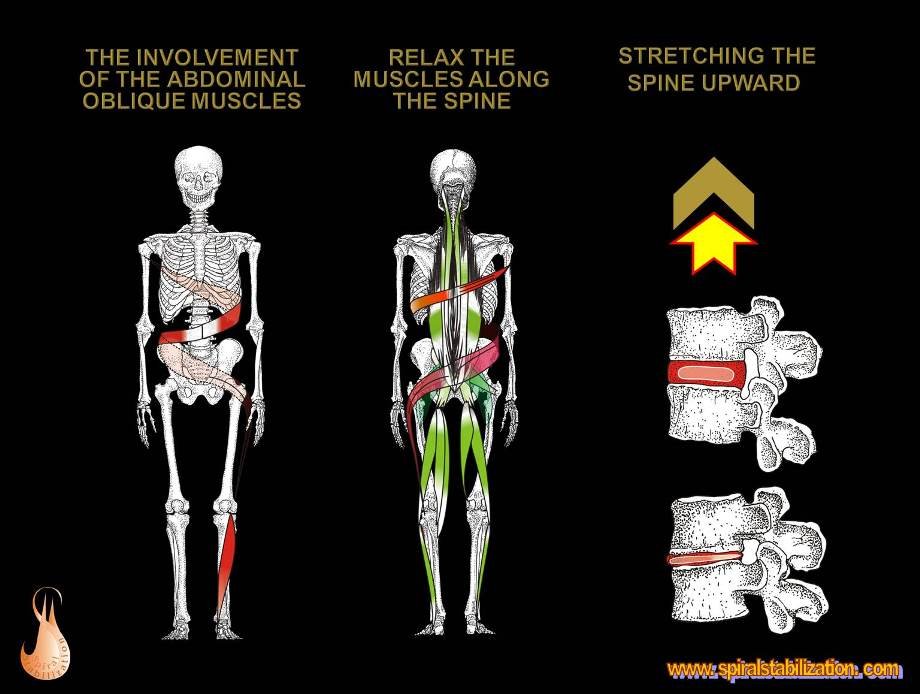
The Spiral Stabilization gradually strengthen the spiral muscle chains and stretches the spine upwards.
The vertical muscles relax and stretch
This helps with mobilization of the spine in rotation with traction.
The Spiral Stabilization improves posture, strengthens important muscles, and allows the intervertebral discs to regenerate more easily.
Definition of Spiral Stabilization terms
Spiral Stabilization is systematic treatment of the human movement apparatus and the function of the internal organs.
Spiral Stabilization combines rehabilitation treatment with prevention, regeneration and conditioning and performance training using single methodological approach – this combination is not provided by any other movement method.
The specialized basis for the method is spirally stabilized movement, which must be performed regularly and integrated into everyday movement practices.
This method is a unique one and brings new knowledge connected with practical applications in sports:
- dynamic stretching with reciprocal inhibition
- dynamic stabilization of the whole body
- optimal stabilization of movement and rest – alternation of spiral and vertical stabilization
- utilizes natural human movement stereotypes – walking, running
Spiral Stabilization relates to nearly all branches of medicine:
– in rehabilitation, it provides the opportunity to treat many diagnoses which have been difficult to manage in the past (scoliosis, spinal stenosis, slipped disc)
– in other fields, it is an effective part of the treatment which enables other treatment means and makes them effective
– it is, at the same time, effective prevention of these diseases
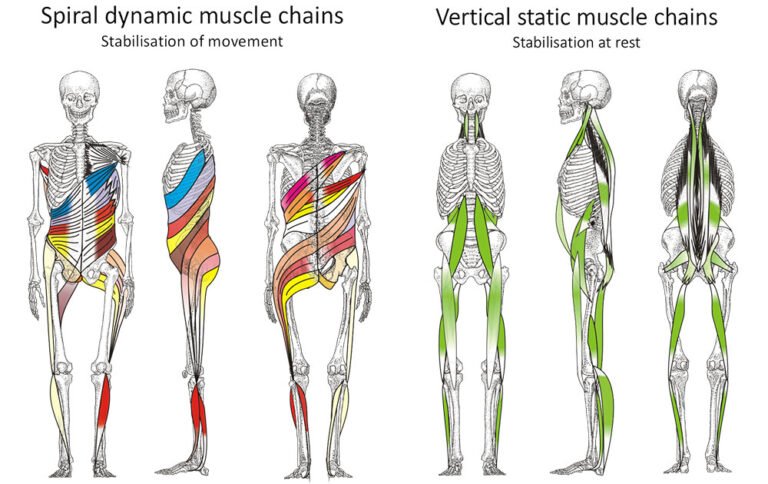
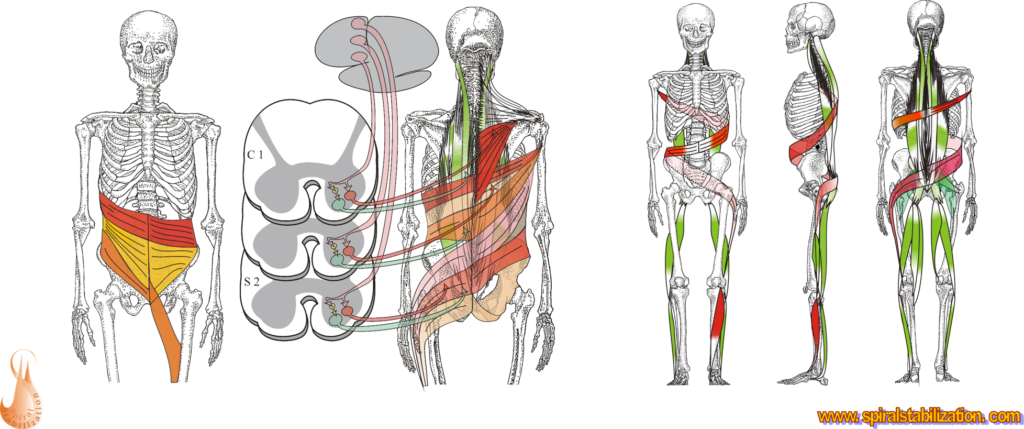
Muscle chains
Vertical – Stabilization at rest
They stabilize body at rest, if they are used during movement, they cause compression and therefore can cause back issues. They are ofthen tight and need stretching and relaxation.
Spiral – Stabilization at movement
They create traction of the spine during the movement and therefore regenerates the spine. They are often weak and need strengthening.
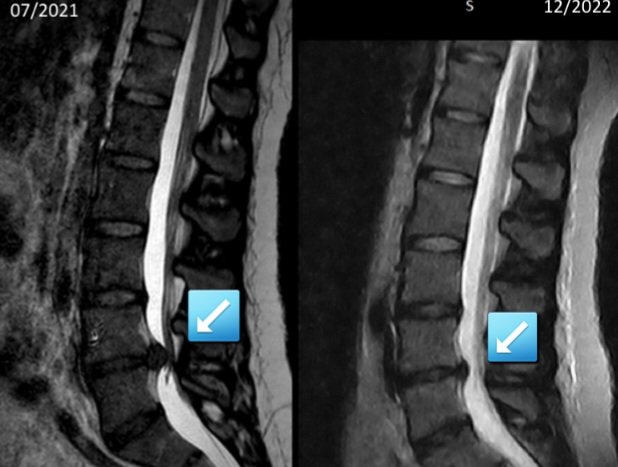
Use of Spiral Stabilization – Diagnosis
The Spiral Stabilization method helps with back pain, scoliosis, disc herniation, or after spinal surgery. It is suitable for all age groups, children from the age of five and also for pregnant women. In addition, it prevents the development of faulty posture and muscle imbalances. Top athletes use Spiral Stabilization to help them improve their sporting performance, recover faster after strain and, above all, achieve sporting success without damaging their health.
Using the muscle chains:
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Condition, Fitness, Wellness
- Sport
Treatment of disorders of the spine:
- Herniation of an intervertebral disc
- Conditions after spinal operations
- Scoliosis
- Hyperlordosis, hyperkyphosis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spinal stenosis
- Scheuermann’s disease
Treatment of disorders of the large joints:
- Hip, knee and ankle joints
- Flat feet, hallux valgus
- Shoulder joint
Disorders of gait coordination and stability:
- Conditions after TEP of the hip or knee joint
- Neuropathy
- Gait disorders in vertebrogenic patients
Disorders of the CNS – central nervous system –caused by disorders of the head posture, tension in the neck muscles and restricted blood supply:
- Headaches
- Giddiness
- Depression
- Burn-out syndrome
- Fatigue syndrome
- Cerebral accidents – apoplexy – part of treatment
Disorders of the PNS – peripheral nervous system:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neuropathy
Cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases:
- Ischemic heart disease
- Hypertension
- Chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma
Gastrointestinal diseases:
- Paralytic ileus – prevention
Metabolic diseases:
- DM II. – diabetes mellitus type II
- Dyslipoproteinemia
Diseases of the muscles and connective tissue:
- Trigger points
- Fibromyalgia
- Systemic disease of the connective tissue
Rheumatic diseases:
- Bekhterev’s disease
- Progressive polyarthritis
Prevention of disorders:
- of the spine
- of the large joints
- of gait stability
- caused by sport
- of the CNS
- of the internal organs – heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, urogenital system
Conditioning, fitness, wellness:
- Axis posture of the body
- Muscle balance
- Reciprocal inhibition of the muscles in motion (active inhibition)
- Sufficient range of motion
- Exercising movement patterns
- Muscle cooperation – exercising the muscle chains
- Developing muscle mass without pressure on the spine – healthy bodybuilding
Sport:
- Fast running speed
- Rapid regeneration of the muscles after sports performance, eliminating trigger points and acidic products
- Effective use of the muscles – movement patterns
- The strength of muscles grows in cooperation with other muscles – potentiation of the muscle in muscle chains
- Rapid muscle contractions with a change in movement – protective function for the joints and spine
Prevention in sport:
- Eliminating muscle imbalances
- After-treatment following accidents and operations
- Compensation of unilateral overloading in sport
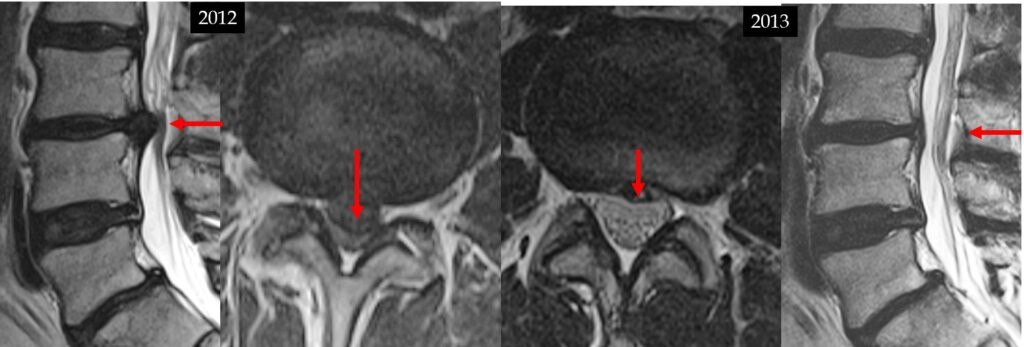
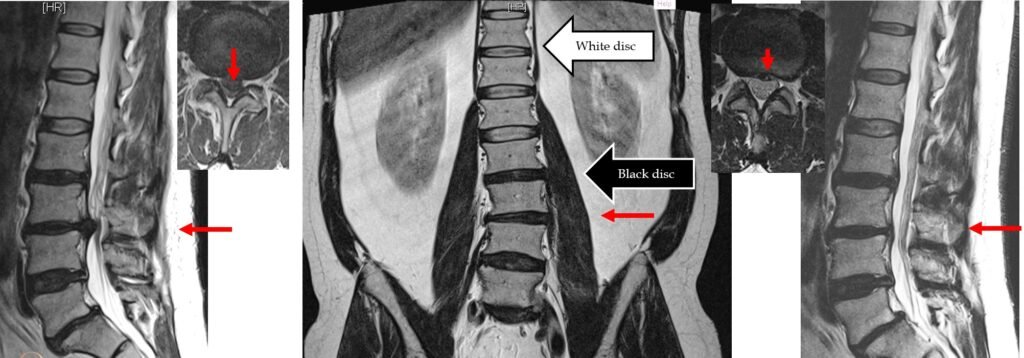
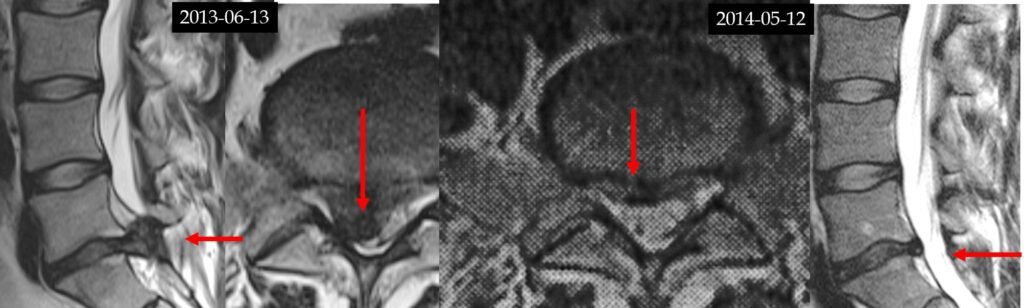
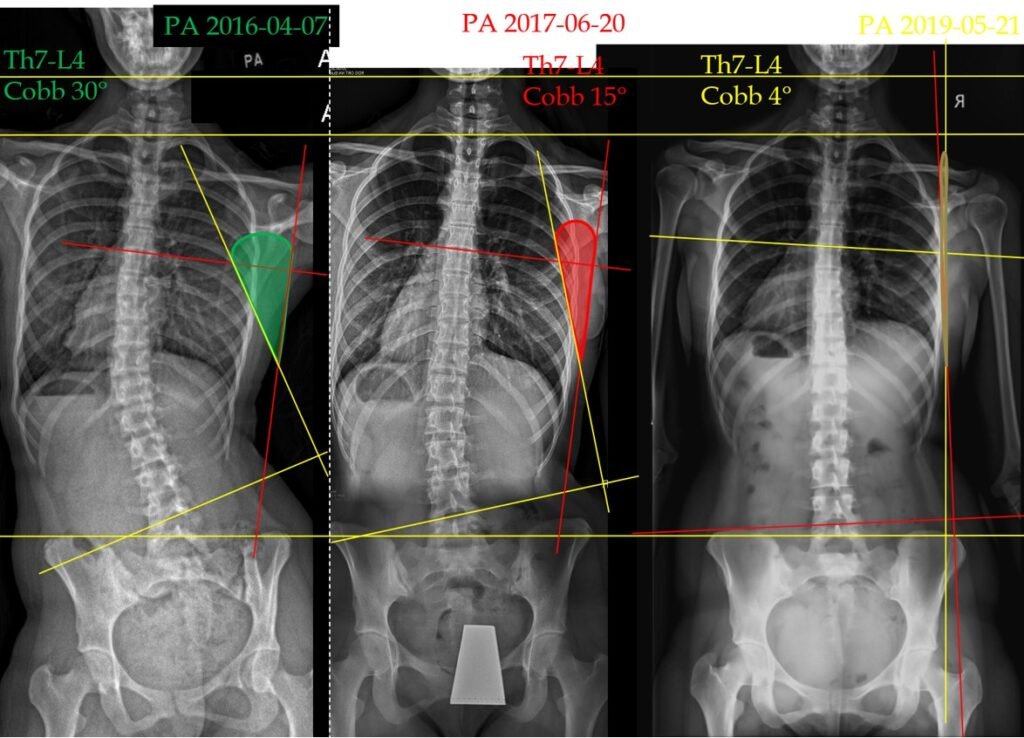
Thank you The Spiral Stabilization rehabilitation clinic in Prague for the provision of some of the images on this page.
You can check even more at http://www.spiralstabilization.com